
This article presents basic concepts in Microsoft Word to help new users get started in creating sophisticated, professional-looking documents.
Start and quit Word
To quit Word, click the x button
in the upper-right corner of your screen.
If you made any changes since you last saved the document, a message box appears asking if you want to save changes. To save the changes, click Yes. To quit without saving the changes, click No. If you clicked the x button by mistake, click Cancel.
A tour of the Word user interface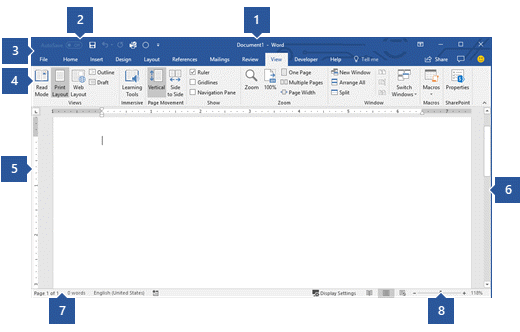
1 Title Bar: Displays the file name of the document that is being edited and the name of the software you are using. It also includes the standard Minimize, Restore, and Close buttons.
2 Quick Access Toolbar: Commands that are frequently used, such as Save, Undo, and Redo are located here. At the end of the Quick Access Toolbar is a pull-down menu where you can add other commonly used or commonly needed commands.
3 File Tab: Click this button to find commands that act on the document itself rather than the content of the document, such as New, Open, Save as, Print, and Close.
4 Ribbon: Commands needed for your work are located here. The appearance of the Ribbon will change depending on the size of your monitor. Word will compress the ribbon by changing the arrangement of the controls to accommodate smaller monitors.
5 Edit Window: Shows the contents of the document you are editing.
6 Scroll Bar: Lets you change the display position of the document you are editing.
7 Status Bar: Displays information about the document you are editing.
8 Zoom slide control: Lets you change the zoom settings of the document you are editing.
Save and open a documentIn Word, you must save your document so you can quit the program without losing your work. When you save the document, it is stored as a file on your computer or in a network location. Later, you can open the file, change it, and print it.
To save a document, do the following:
You can open a Word document to resume your work. To open a document, do the following:
Tip: You can also open a document from within Word by clicking the File tab and then clicking Open. To open a document you saved recently, click Recent.
Edit and format textBefore you edit or format text, you must first select the text. Follow the steps below to select text.
You can find most text formatting tools by clicking the Home tab and then choosing from the Font group.
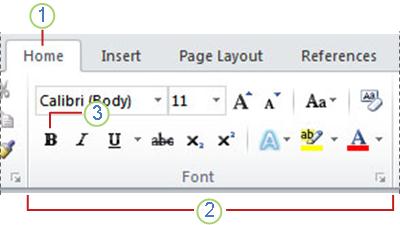
1 This is the Home tab.
2 This is the Font group on the Home tab.
3 This is the Bold button. See the table below for the names and functions of all the buttons in the Font group.

Changes the font.

Changes the size of the text.

Increases the text size.

Decreases the text size.

Change all the selected text to uppercase, lowercase, or other common capitalizations.

Clears all formatting for the selected text, leaving only the plain text.

Makes the selected text bold.
Italicizes the selected text.

Draws a line under the selected text. Click the dropdown arrow to select the type of underline.

Draws a line through the middle of selected text.

Creates subscript characters.

Creates superscript characters.

Apply a visual effect to selected text, such as shadow, glow, or reflection.

Text Highlight Color
Makes text look like it was marked with a highlighter pen.

Changes the text color.
Use stylesStyles allow you to quickly format major elements in your document, such as headings, titles, and subtitles. Follow the steps below to apply styles to the text in your document.
When you’re done applying styles to the individual elements, Word lets you use a style set to change the look of your whole document all at once.
With Word, you can easily change the spacing between lines and paragraphs in your document.
Tip: To define your own paragraph spacing, choose Custom Paragraph Spacing.
Preview and printIt’s easy to preview what the layout of your document will look like when printed without actually printing.